ZeroDAO Network
- Team Name: ZeroDAO
- Payment Address: 0xEBCDa7c73EB5Dd7a4314cFf395bE07EB1E24c046
Project Overview 📄
Overview
We define ZeroDAO as a public resource, including a social network, a reputation system. the ZeroDAO social network solves the incentive dilemma that currently exists in blockchain social networks, while incentivizing good behavior makes good behavior disappear. Imagine what Twitter would look like if you could get $1 for posting a tweet. Two-factor theory even concludes that security, salary, fringe benefits, good pay is not Motivators but Hygiene factors. Hygiene factors that do not give positive satisfaction or lead to higher motivation.
ZeroDAO social network solves the incentive dilemma by amplifying social motivation and internalizing external motivation.
In the ZeroDAO network, we still quantify user contributions and settle them into Tokens, which we call social currency. It is frozen and at some point assigned to users trusted by the owner, it is also social currency and goes on to be shared. The user's social motivation is amplified. We use to shared information, now we share value.
ZeroDAO social network brought us the reputation system and we proposed the TIR algorithm to compute the graph and obtain the reputation of each user. TIR is difficult to compute but easy to verify on-chain. This feature makes ZeroDAO's reputation system completely decentralized. At the same time, it has strong ability to prevent Sybil Attack to meet the security needs of financial products and on-chain governance. ZeroDAO also brings credit finance, zero-cost payments, and other applications to the blockchain.
Project Details
Social Network

- The application quantifies user contributions and transfer social currency to A. Pending Token is frozen and cannot be used.
- The system periodically distribution of A's social currency to its trusted [B,C,D]. A small part of social currency is unlocked to the owner.
- Forming a value-sharing network. B, C & D also share their social currency, forming a value sharing network.
Social Currency

ReserveReserve the owner's free balance. The percentage can be adjusted by the community.ShareTransfer to the social currency of users trusted by the owner.FeeAnalyst's fee.BurnShare to all users.Reward poolUsed to solve the verifier's Dilemma.
Reputation System
TIR( Trust-Influence-Reputation ) Algorithm
The TIR algorithm is inspired by Google's text retrieval algorithm for search engines. It is used to replace the vulnerable PageRank algorithm and has similar capabilities to TrustRank, but is simpler to compute and requires no iterations. TIR draws on its idea by finding high-impact users in the network as seed users, setting the highest score for them, and then passing the reputation on to other users through trust relationships.
The TIR algorithm relies on two assumptions
- High-influence users are less likely to trust fake users
- The longer the trust, the more credible it is
Procedures of calculation

- The set of nodes with the largest number of passes through all the longest shortest paths in the graph is selected as the seed users. The larger the network and the higher the account retention amount, the more difficult it is to cheat.
- For example, we want to calculate the reputation of user
D. - Set the reputation of the seed user to 𝑅max , get the reputation of the seed user in the last round 𝑅seed0.
- Calculate the shortest weighted path
Seed -> A -> Dfrom the seed user to theDuser. - The path weight is the natural logarithm of the difference between the reputation values of the two users in the last round, and the minimum value is
1. - Calculate the reputation 𝑅a1 passed at node
A: Take the initial reputation value of Seed, divide it by the number of users Trusted by Seed, and divide it by the path weight. - Calculate the path weight from node
Ato nodeDin the same way and calculate the reputation of the final pass to nodeD. The sum of the reputation values of all seed passes is the final reputation of the target user.
Easy to verify
The TIR algorithm is extremely resource intensive to run on the blockchain, but verification is very simple, with the core verification requiring only 20 or so lines of code in substrate.
Sybil Attack resistance
So far, the algorithm is still not able to prevent Sybil Attacks.
The algorithm will pick to cheat nodes when the attacker constructs a graph that is more favorable to it (e.g. more fake nodes and trust). Although we can raise the cost of an attack by setting higher account retention balances, raising fees, or raising gas, and expecting the network to be large enough so that the attacker does not have enough wealth or benefit to attack the network. But this also raises the cost for honest users, which is not elegant, and does not guarantee mathematical security.
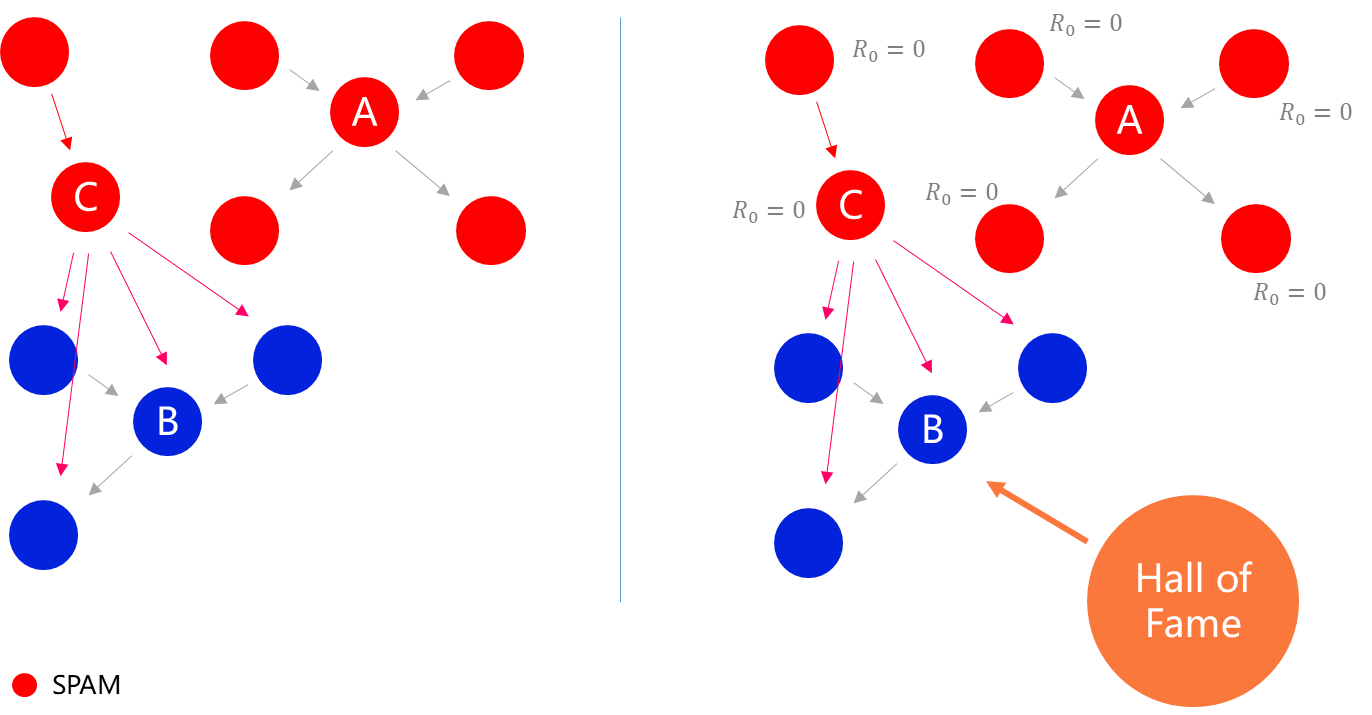
Hall of Fame
ZeroDAO uses a simple approach. By electing the Hall of Fame through the community, the distance from the Hall of Fame is added to the seed selection algorithm. The attacker has zero or very little reputation, while users who need more than a certain reputation can participate in the election. The attacker cannot join the Hall of Fame and cannot be seed, and the attack fails. We computed circles, a social network with 100,000 on-chain users, which was also subject to sybil attacks. We selected only 20 Hall of Fame users and the algorithm worked well. You can find the calculation results here for round3 without the Hall of Fame, and round4 with the Hall of Fame.
challenge
The reputation system is implemented through a challenge model. The system has two roles, analyst and validator. The analyst updates the reputation after staking. The validator monitors the correctness of the data and can challenge the result after staking and upload the path. At this point the system still does not compute the path. Other validators, if they find errors in it, only need to point out errors in individual paths. The system verifies the calculations and determines who is correct at this time. The sub-challenge mode significantly improves the efficiency of the system.

collusion attack
Collusion only affects social finance and has little to no impact on reputation systems. The collusion attack here is the unlock of social currency that should be frozen through dishonest trust relationships. First, ZeroDAO allows users to not share, just like in the real world, where they have the right not to share but lose certain conveniences in using the eco-product. We have the following options.
Minimum number of trusts: For example, if Alice trusts 3 users and the minimum number of trusts is 20, then the amount allocated to each user is not 1/3 but 1/20 of the total amount. the remaining part is waiting for the next allocation. So users who do not want to share only need to trust as few other users as possible. After the minimum trust number is exceeded, the amount will be split very small and transaction costs (gas) will become significant.Burn: Partial burn substantially increases the cost of evil nodes.Front-end SDK: Wallets or security agencies can monitor user behavior off chain, give warning messages in the UI for risky users, and prevent other users to trust.Negative propagation: The TIR algorithm supports propagating negative values to users who trust the evil user.
Applications
The social finance, reputation system and zero-cost payment will lead to many exciting applications.
- Traditional social network transformation: The ZeroDAO network doesn't care where the Dapp's data is stored, so it is very adaptable and traditional social networks only need to add a
Trustbutton to connect to the ZeroDAO network. - Radical Social Network: Reputation systems and trust relationships make possible a new model of social networking, and we propose a reverse communication social network, where users post content that is not pushed to the feeds of their followers, but to the feeds of their trusted people. This may sound difficult to understand, but if you look at it in detail, you will see that this is an exciting new social network, as explained in more detail in the light white paper.
- Governance: Sybil have been blocked, and now you can safely use the Quadratic Voting (e.g. Quadratic funding platform). You can also go experiment with more interesting modes of governance.
- Super Bank: Super bank is another banking model other than central bank, commercial bank. It runs on blockchain through smart contracts, it has credit financial capability, directly facing users, instantly sensing user behavior, and adjusting interest rate with every transaction. It has deterministic expectations, including a flexible total amount of issuance, deterministic interest rate changes, and therefore can effectively sense the economic crisis. Even in the event of an economic crisis, he possesses deterministic self-recovery. It is finding equilibrium in every transaction, so there is no Minsky moment.
- Zero-cost payment: A payment model where the user didn't pay anything. Especially when the minimum trust number is exceeded. Social finance includes institutional accounts, which do not participate in the calculation of the reputation system and are allocated the amount directly to the free balaner. users have nothing to lose in the payment process, thus increasing the participation rate of the charity. It is very useful in other donations, such as donations to open source communities. However, it is currently limited to payments to trusted institutions, and large-scale commercial use ( e.g. in pay-per-month music applications, decentralized storage payments ) needs to Solving collusion attack.
Ecosystem Fit
Social Network
There are about 20+ well-known blockchain social networks, which we did research on in 2020, and ZeroDAO's social network is different from them in the following ways.
ZeroDAO social finance is the underlying economic system
We don't care about the product form of the social network, whether it has comments, how the content is presented, how users interact, etc., or how he stores it, whether it uses IPFS or exists on its own servers. We only work on the more core and underlying economic systems and user relationships.
ZeroDAO's incentive model has been radically improved
Reputation System
A reputation system built on a blockchain essentially refers to the extent to which the system can trust a user. A reputation system in a broad sense includes identity verification, credit rating, and so on. There are a very large number of projects that intend to build reputation systems, and there are several broad categories, each with corresponding case; for the sake of brevity, specific applications are not listed here.

- Evaluation: Two types are included, one with specific purposes, such as evaluation between buyers and sellers in a buying relationship, evaluation between DAO collaboration members, evaluation between demand and supply sides in a Witkey system. The problem is the low coverage and poor data standardization. The other type is voting without a specific purpose, which suffers from the problem that users lack a fundamental motivation to vote. Overall, it is also a good direction if there is a simple and effective enough way to counter attacks and standardize all data from an ecological point of view. In comparison, ZeroDAO has more coverage, more uniform data, and more security.
- Personal Currency: Applications based on personal currencies are usually able to guarantee the validity of the relationship through certain economic models. This is one of the better categories to build a reputation system, and in fact, ZeroDAO's previous solution used exactly this approach. Each user can issue a personal currency and add liquidity in the form of x * y = k. A trust relationship graph is constructed between users through a complex economic system. However, in discussions with the community, it became clear that we were imposing too much responsibility on users, making them very confused about the act of trust. The most fundamental problem with this approach is that its security relies too much on the design of the economic system and always assumes that the economic system works perfectly. In fact, the incomplete contract will induce to constant problems in complex economic systems. The economic system would have to be tired of tinkering with and making the economic system more and more complex. We have abandoned this approach.
- Social Network: ZeroDAO's reputation system is built on top of that. Most blockchain social networks claim to be able to build reputation systems. But computing centrality on-chain consumes too many resources. When the network is large, it is still too expensive even for Off-Chian Workers. ZeroDAO combines an economic system with the TIR algorithm to achieve a truly high-availability, sybil-resistant reputation system.
- Other: It is also possible to build a reputation system by means of a computational marketplace similar to
TrueBitthat computes some kind of data on a large scale. There is already a peer-review based project being built. However, TrueBit's calculation method itself has some limitations.
ZeroDAO reputation system is positioned as the core of a on-chain reputation system to meet the needs of most applications and has a high adoption rate. It is simple and reliable and does not require cumbersome operations for users. Third parties can also add other reputation systems on top of ZeroDAO reputation system according to their needs.
Team 👥
Team members
- Daqin Lee
- Zhidong Chen
Contact
- Contact Name: Daqin Lee
- Contact Email: lee@0p0.org
- 0p0.org
Team's experience
Daqin Lee: Full-stack Developer,Rust And Substrate Developer
Chen Zhidong: Full-stack Developer, Tesla Machine Learning Engineer,GoHack 2017 Hackathon First Prize
Team Code Repos
Development Status 📖
Algorithm validation
We built a simple application to validate the algorithm and perform tuning, and show the results of the computation. It synchronized Circles-UBI on-chain user data and relationship data from theGraph, and we simulated the calculation of reputation for all users using the TIR algorithm and also calculateds Betweenness Centrality, PageRank, Article Rank, Degree Centrality, Harmonic Centrality, Eigenvector Centrality, Closeness Centrality.
We computed data at different data sizes several times in our development environment. And a website was deployed to demonstrate how the selection of Hall of Fame users affects the calculation. You can also query the reputation of any user in the application, as well as the shortest path between users. We are still tuning the algorithm, so if you find significant deviations in the data, please contact us.
Website: https://socircles.info
Front-end: https://github.com/ZeroDAO/socircles-ui
Back-end: https://github.com/ZeroDAO/socircles-backend
Management: https://github.com/ZeroDAO/socircles-admin
White Paper
We currently have a light white paper.
Development Roadmap 🔩
Overview
- Total Estimated Duration: 7 weeks
- Full-Time Equivalent (FTE): 3.5 FTE
- Total Costs: 15,000 DAI
Milestone 1 Example — Implement Substrate Modules
- Estimated duration: 7 weeks
- FTE: 3.5
- Costs: 15,000 DAI
| Number | Deliverable | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| 0a. | License | Apache 2.0 / MIT / Unlicense |
| 0b. | Documentation | We will provide both inline documentation of the code and a basic tutorial that explains how a user can (for example) spin up one of our Substrate nodes. Once the node is up, it will be possible to send test transactions that will show how the new functionality works. And a tutorials on when to use social finance design guidelines. |
| 0c. | Testing Guide | We will provide a full test suite and guide for ZeroDAO node manage |
| 1. | Pallet: refresh-reputation | Refresh user's reputation |
| Storage | Fees: StorageMap<_, Twox64Concat, T::AccountId, (u32, Balance), ValueQuery>;Records: StorageDoubleMap<_, Twox64Concat, T::AccountId, Twox64Concat, T::AccountId, Record<T::BlockNumber,Balance>, ValueQuery>; | |
| Struct | pub struct Record<BlockNumber,Balance> | |
| Functions | pub fn new_round(origin: OriginFor<T>) -> DispatchResultWithPostInfopub fn refresh_reputation(origin: OriginFor<T>, user_scores: Vec<(T::AccountId,u32)>) -> DispatchResultWithPostInfopub fn receiver_all(origin: OriginFor<T>) -> DispatchResultWithPostInfo | |
| 2. | Pallet: reputation | Maintain the user's reputation for the last two rounds and set reputation system information |
| Storage | SystemInfo: StorageValue<_, OperationStatus<T::BlockNumber>, ValueQuery>LastChallenge: StorageValue<_, T::BlockNumber, ValueQuery>ReputationScores: StorageMap<_, Twox64Concat, T::AccountId, [ReputationScore;2], ValueQuery> | |
| Struct | pub struct OperationStatus<BlockNumber>pub struct ReputationScore | |
| Functions | pub fn set_duration(origin: OriginFor<T>,duration: T::BlockNumber) -> DispatchResultWithPostInfofn mutate_reputation(target: &T::AccountId, reputation: u32)fn new_round() -> DispatchResultfn get_reputation_new(target: &T::AccountId) -> Option<u32>fn refresh_reputation(user_score: &(T::AccountId,u32),round: u32) -> DispatchResultfn last_refresh_at(now: &T::BlockNumber)fn check_update_status(update_mode: bool) -> Option<u32>fn last_challenge_at(now: &T::BlockNumber)fn end_refresh(now: &T::BlockNumber) -> DispatchResult | |
| 3. | Pallet: seeds | A simple function to set seed user for root account |
| Storage | Seeds: StorageMap<_, Twox64Concat, T::AccountId, u32, ValueQuery>;SeedsCount: StorageValue<_, u32, ValueQuery>; | |
| Functions | pub fn add_seed(origin: OriginFor<T>,new_seed: T::AccountId) -> DispatchResultWithPostInfopub fn remove_seed(origin: OriginFor<T>, seed: T::AccountId) -> DispatchResultWithPostInfofn get_seed_count() -> u32fn is_seed(seed: &T::AccountId) -> bool | |
| 4. | Pallet: trust | Allows users to manage trust relationships, cache relationship data during reputation refreshes, calculate user paths and scores |
| Storage | TrustedList: StorageMap<_, Twox64Concat, T::AccountId, UserSet<T::AccountId>, ValueQuery>;TrustTempList: StorageMap<_, Twox64Concat, T::AccountId, TrustTemp<T::AccountId>, ValueQuery>; | |
| Struct | pub struct TrustTemp<AccountId> | |
| Functions | pub fn trust(origin: OriginFor<T>, target: T::AccountId) -> DispatchResultWithPostInfopub fn untrust(origin: OriginFor<T>, who: T::AccountId, target: T::AccountId) -> DispatchResultWithPostInfofn get_trust_count(who: &T::AccountId) -> usizefn get_trust_count_old(who: &T::AccountId) -> usizefn is_trust(who: &T::AccountId, target: &T::AccountId) -> boolfn is_trust_old(who: &T::AccountId, target: &T::AccountId) -> boolfn get_trust_old(who: &T::AccountId) -> Vec<T::AccountId>fn computed_path(users: &Vec<T::AccountId>) -> Result<(u32,u32), DispatchError> | |
| 5. | Pallet: challenges | Allow users to initiate a challenge or sub-challenge after staking, the system verifies the sub-challenge, and the challenge is successful to receive the earnings. |
| Storage | Challenges: StorageMap<_, Twox64Concat, T::AccountId, Challenge<T::AccountId, T::BlockNumber>, ValueQuery>;LastUpdate: StorageValue<_, T::BlockNumber, ValueQuery>;SubChallenges: StorageMap<_, Twox64Concat, T::AccountId, Progress<T::AccountId>, ValueQuery>;Paths: StorageDoubleMap<_, Twox64Concat, T::AccountId, Twox64Concat, T::AccountId, Path<T::AccountId>, ValueQuery>; | |
| Struct | pub struct Poolpub struct Progress<AccountId>pub struct Challenge<AccountId, BlockNumber>pub struct Path<AccountId> | |
| Functions | pub fn start_challenge(origin: OriginFor<T>, target: T::AccountId, analyst: T::AccountId, quantity: u32) -> DispatchResultWithPostInfopub fn upload_path(origin: OriginFor<T>,target: T::AccountId,seeds: Vec<T::AccountId>,paths: Vec<Path<T::AccountId>>) -> DispatchResultWithPostInfopub fn start_sub_challenge(origin: OriginFor<T>, target: T::AccountId, quantity: u32) -> DispatchResultWithPostInfopub fn receiver_challenge(origin: OriginFor<T>, target: T::AccountId) -> DispatchResultWithPostInfo | |
| 6. | Front End | Complete the development of the basic interactive page in vue,and the interface will be available in Chinese as well as English. |
| 7. | Substrate chain | All the above modules of our custom chain will interact with each other to provide an MVP. there will be APIs to set seeds, allow sending social currency to users, update reputation, launch challenges and receive earnings. |
| 8a. | Docker | We will provide a Dockerfile to demonstrate the full functionality of our chain |
| 8b. | Article | We will write an article or tutorial that explains the work done as part of the grant. |
Future Plans
short term
- Alpha Network
- Algorithm tuning
- Solving the Verifier's Dilemma
- Optimize economic system design
- Integrating Quadratic Voting, MACI and Reputation Governance to Launch Hall of Fame Voting
- Implement seeding algorithm for user selection
long term
-
Ecosystem

-
Brand And Market: Achieving the positioning of public resources
-
DAO: Operates entirely through DAO
Additional Information ➕
How did you hear about the Grants Program? Announcement by another team.
- Wheter there are any other teams who have already contributed (financially) to the project.
- No
- Previous grants you may have applied for.
- No